Introduction
The FlowLayout is used to arrange the components in a line, one after another (in a flow). It is the default layout of applet or panel.
Class Declaration
Following is the declaration for java.awt.FlowLayout class −
public class FlowLayout
extends Object
implements LayoutManager, Serializable
Field
Following are the fields for java.awt.BorderLayout class −
- static int CENTER − This value indicates that each row of components should be centered.
- static int LEADING − This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the leading edge of the container's orientation. For example, to the left in left-to-right orientations.
- static int LEFT − This value indicates that each row of components should be left-justified.
- static int RIGHT − This value indicates that each row of components should be right-justified.
- static int TRAILING − This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the trailing edge of the container's orientation. For example, to the right in left-to-right orientations.
Class Constructors
| Sr.No. | Constructor & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
FlowLayout()
Constructs a new FlowLayout with a centered alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap.
|
| 2 |
FlowLayout(int align)
Constructs a new FlowLayout with the specified alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap.
|
| 3 |
FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap)
Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment and the indicated horizontal and vertical gaps.
|
Class Methods
| Sr.No. | Method & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)
Adds the specified component to the layout.
|
| 2 |
int getAlignment()
Gets the alignment for this layout.
|
| 3 |
int getHgap()
Gets the horizontal gap between the components.
|
| 4 |
int getVgap()
Gets the vertical gap between the components.
|
| 5 |
void layoutContainer(Container target)
Lays out the container.
|
| 6 |
Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target)
Returns the minimum dimensions needed to layout the visible components contained in the specified target container.
|
| 7 |
Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target)
Returns the preferred dimensions for this layout given the visible components in the specified target container.
|
| 8 |
void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
Removes the specified component from the layout.
|
| 9 |
void setAlignment(int align)
Sets the alignment for this layout.
|
| 10 |
void setHgap(int hgap)
Sets the horizontal gap between the components.
|
| 11 |
void setVgap(int vgap)
Sets the vertical gap between the components.
|
| 12 |
String toString()
Returns a string representation of this FlowLayout object and its values.
|
Methods Inherited
This class inherits methods from the following classes −
- java.lang.Object
FlowLayout Example
Create the following Java program using any editor of your choice in say D:/ > SWING > com > sjavaspot> gui >
SwingLayoutDemo.java
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; public class SwingLayoutDemo { private JFrame mainFrame; private JLabel headerLabel; private JLabel statusLabel; private JPanel controlPanel; private JLabel msglabel; public SwingLayoutDemo(){ prepareGUI(); } public static void main(String[] args){ SwingLayoutDemo swingLayoutDemo = new SwingLayoutDemo(); swingLayoutDemo.showFlowLayoutDemo(); } private void prepareGUI(){ mainFrame = new JFrame("Java SWING Examples"); mainFrame.setSize(400,400); mainFrame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); headerLabel = new JLabel("",JLabel.CENTER ); statusLabel = new JLabel("",JLabel.CENTER); statusLabel.setSize(350,100); mainFrame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent windowEvent){ System.exit(0); } }); controlPanel = new JPanel(); controlPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); mainFrame.add(headerLabel); mainFrame.add(controlPanel); mainFrame.add(statusLabel); mainFrame.setVisible(true); } private void showFlowLayoutDemo(){ headerLabel.setText("Layout in action: FlowLayout"); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setBackground(Color.darkGray); panel.setSize(200,200); FlowLayout layout = new FlowLayout(); layout.setHgap(10); layout.setVgap(10); panel.setLayout(layout); panel.add(new JButton("OK")); panel.add(new JButton("Cancel")); controlPanel.add(panel); mainFrame.setVisible(true); } }THE OUTPUT:
THE OUTPUT:
- import java.awt.*;
- import javax.swing.*;
- public class MyFlowLayout{
- JFrame f;
- MyFlowLayout(){
- f=new JFrame();
- JButton b1=new JButton("1");
- JButton b2=new JButton("2");
- JButton b3=new JButton("3");
- JButton b4=new JButton("4");
- JButton b5=new JButton("5");
- f.add(b1);f.add(b2);f.add(b3);f.add(b4);f.add(b5);
- f.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
- //setting flow layout of right alignment
- f.setSize(300,300);
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- new MyFlowLayout();
- }
- }
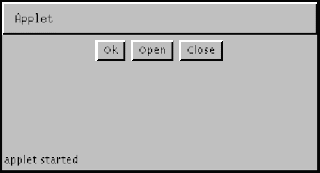
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class myButtons extends Applet {
Button button1, button2, button3;
public void init() {
button1 = new Button("Ok");
button2 = new Button("Open");
button3 = new Button("Close");
add(button1);
add(button2);
add(button3);
}
}




great
ReplyDelete